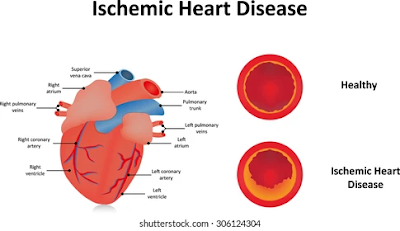
1) Ischaemic Heart Disease:
This is a condition that occurs when the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked, leading to decreased blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart. Risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
2) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
COPD is a group of lung diseases that cause breathing difficulties due to inflammation and obstruction of the airways. Smoking is the primary cause of COPD, but exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemical fumes can also contribute to its development.
3) Lower Respiratory Infections:
Lower respiratory infections refer to infections of the lungs and airways, such as pneumonia and bronchitis. These infections are caused by bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens, and can be more severe in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly and young children.
4) Stroke:
A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain damage and often resulting in long-term disability or death. Risk factors include high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
5) Tuberculosis:
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. TB spreads through the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and is more common in areas with poor ventilation and crowded living conditions.
6) Neonatal encephalopathy:
7) Diarrheal Diseases:
8) Diabetes mellitus:
9) Kidney Diseases:
Kidney disease refers to damage or dysfunction of the kidneys, often caused by chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. In India, high rates of these conditions and poor access to healthcare contribute to the high burden of kidney disease.
10) Liver Diseases:
Liver diseases can be caused by various factors, including alcohol consumption, viral infections, and obesity. In India, viral hepatitis infections are a significant contributing factor to liver disease.
Medications To Cure:
· Ischemic Heart Disease: Treatment for ischemic heart disease usually includes lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, as well as medications such as antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and statins. In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary.
· Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): COPD is typically managed with bronchodilators, steroids, and other respiratory medications. In severe cases, oxygen therapy may be necessary.
· Stroke: Stroke treatment often includes medications to prevent blood clots, such as aspirin or anticoagulants. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a blood clot or repair a damaged blood vessel.
· Lower Respiratory Infections: Treatment for lower respiratory infections may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, or other supportive therapies such as oxygen therapy.
· Diarrheal Diseases: Treatment for diarrheal diseases typically includes rehydration therapy, which may involve oral rehydration salts, intravenous fluids, or a combination of both. Antibiotics may be necessary in some cases.
· Tuberculosis: Treatment for tuberculosis typically involves a combination of antibiotics, often over several months. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove infected tissue.
· Neonatal Disorders: The treatment for neonatal disorders will depend on the specific condition, but may involve medications, surgery, or other supportive therapies.
· Liver Disease: The treatment for the liver disease will depend on the specific condition, but may involve medications, dietary changes, or in some cases, surgery.
· Preterm Birth Complications: Treatment for preterm birth complications may involve medications to delay labor, supportive therapies for the baby such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, or in some cases, surgery.
· Kidney Disease: The treatment for kidney disease will depend on the specific condition, but may involve medications, dietary changes, or in some cases, dialysis or kidney transplant.
It's important to note that this is just a general overview of the treatments for these conditions and that the specific treatment plan will depend on the individual case and should be determined by qualified healthcare.
Written By Narayanamanikandan B


















0 Comments